Temperature Sensor Basics
by:Kaidi Sensors
2022-10-09
Temperature sensors are widely used. The following are some basic knowledge and common terms of temperature sensors. 1. Output impedance: The impedance measured at the sensor output when the input is short-circuited. 2. Zero output: Under city conditions, the output of the sensor when the added measured value is zero. 3. Hysteresis: Within the specified range, when the measured value increases and decreases, the maximum difference that appears in the output. 4. Late: The time delay of the output signal change relative to the input signal change. 5. Drift: During a certain time interval, the sensor output is finally measured irrelevant and unwanted variation. 6. Zero drift: the change in zero output at a specified time interval and indoor conditions. 7. Sensitivity: the ratio of the increment of the sensor output to the corresponding increment of the input. 8. Sensitivity drift: The change in the slope of the calibration curve due to the change in sensitivity. 9. Thermal Sensitivity Drift: Sensitivity drift due to changes in sensitivity. 10. Thermal Zero Drift: Zero drift due to changes in ambient temperature. 11. Linearity: The degree to which the calibration curve conforms to a specification only. 12. Philippine linearity: The degree to which the calibration curve deviates from a specified straight line. 13. Long-term stability: the ability of the sensor to remain within the allowable error for a specified time. 14. Inherent rate: when there is no resistance, the sensor's free (without external force) oscillation rate. 15. Response: The characteristic of the measured change at the output. 16. Compensated temperature range: The temperature range that is compensated for the sensor to maintain zero balance within the span and specified limits. 17. Creep: The change in output within a specified time when the measured machine has a constant environmental condition. 18. Insulation resistance: Unless otherwise specified, it refers to the resistance value measured between the specified insulating parts of the sensor when the specified DC voltage is applied at room temperature. 19. Sensor: A device or device that can sense the specified measured value and convert it into a usable output signal according to a certain law. Usually consists of sensitive components and conversion components. ①Sensitive element refers to the part of the sensor that can be measured directly (or in response). ② The conversion element refers to the part of the electrical signal that can be sensed (or responded) by a more sensitive element in the sensor and converted into an electrical signal that is transmitted and (or) measured. ③ When the output is a specified standard signal, it is called a transmitter. 20. Measuring range: the range of the measured value within the allowable error limit. 21. Range: The algebraic difference between the upper and lower limit of the measurement range. 22. Accuracy: The degree to which the measured result agrees with the true value. 23. Repeatability: The degree of agreement between the results of multiple consecutive measurements of the same quantity under all the following conditions: Same method of measurement: Same observer: Same measuring instrument: Same location: Same conditions of use: repetition in a short period of time. 24. Resolution: The minimum change that the sensor can detect within the specified measurement range. 25. Threshold: The minimum change in a measurand that produces a measurable change at the sensor output. 26. Zero position: the state where the absolute value of the output is minimized, such as a balanced state. 27. Excitation: The external energy (voltage or current) applied to make the sensor work properly. 28. Maximum excitation: The maximum value of excitation voltage or current that can be applied to the sensor under urban conditions. 29. Input impedance: The impedance measured at the input terminal of the sensor when the output terminal is short-circuited. 30. Output: The amount of electricity produced by the sensor as a function of the applied measured value.
KAIDI allocates customer service resources to the platform where their customers are most vocal.
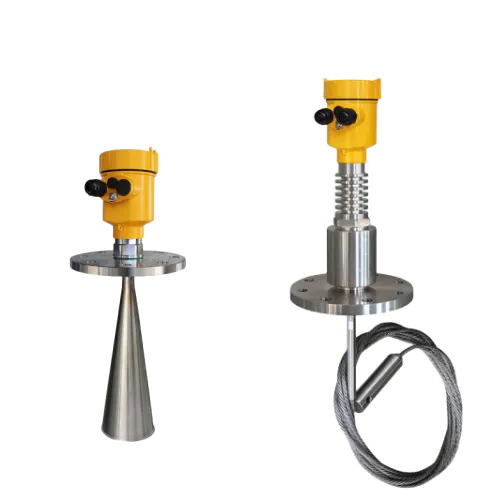
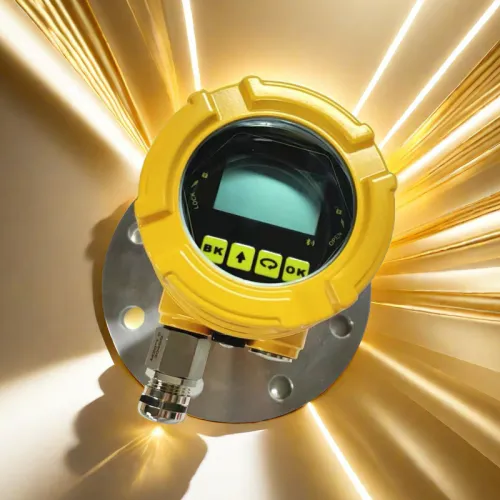
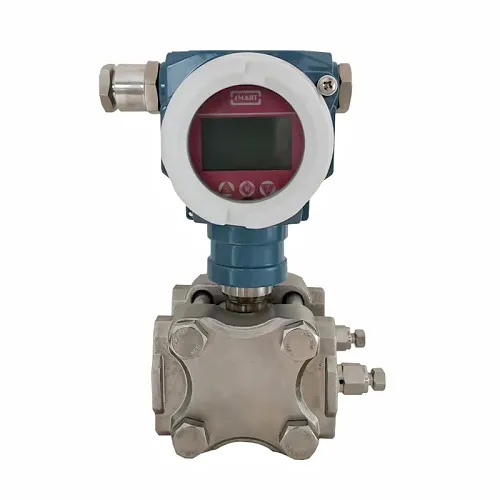
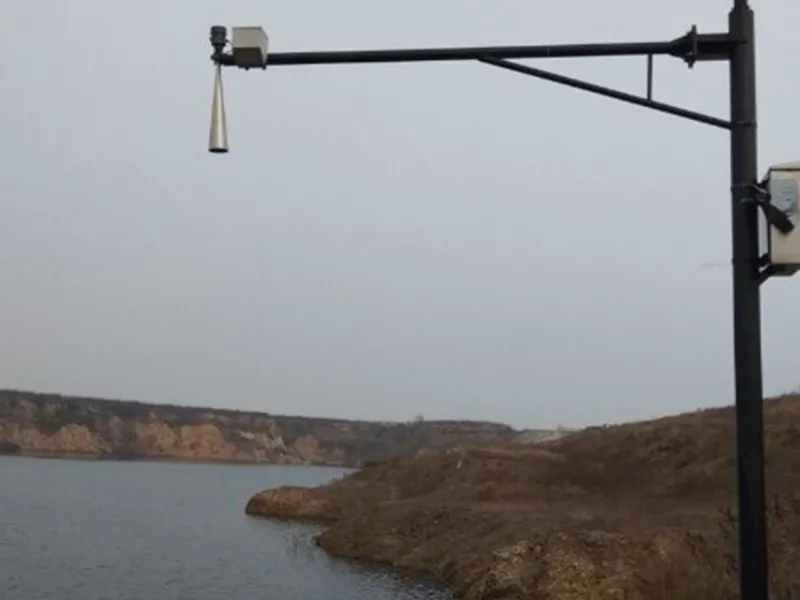
If you already use level gauge elsewhere or want the ability to offer restricted chat access to certain individuals, level gauge customized level indicator offers you the most flexibility.
customized level indicator level gauge are primarily used for customized level indicator.
KAIDI allocates customer service resources to the platform where their customers are most vocal.
If you already use level gauge elsewhere or want the ability to offer restricted chat access to certain individuals, level gauge customized level indicator offers you the most flexibility.
customized level indicator level gauge are primarily used for customized level indicator.
Custom message