BETTER TOUCH BETTER BUSINESS
Contact Sales at KAIDI.
Magnetic flip-plate level gauges and magnetostrictive level gauges are two types of liquid level measurement instruments widely employed in industrial applications. Although both operate on magnetic principles, they exhibit significant differences in working principles, application scenarios, and accuracy. This article will explore these distinctions in detail, incorporating analysis from relevant literature.
I. Working Principles
Magnetic flip-plate level gauge

Magnetic flip-plate level gauges indicate liquid levels through magnetic flip-plates driven by a float that rises and falls with the liquid level. They primarily consist of a magnetic float and an external indicator housing magnetic flip-plates. As the liquid level rises or falls, the magnet within the float pushes the external flip-plates to flip, thereby providing a visual indication of the liquid level height. Since the flipping of the magnetic plates synchronises with the float's movement, users can read liquid level changes in real time. This device requires no external power supply, relying primarily on mechanical and magnetic coupling principles, making it suitable for straightforward liquid level indication.
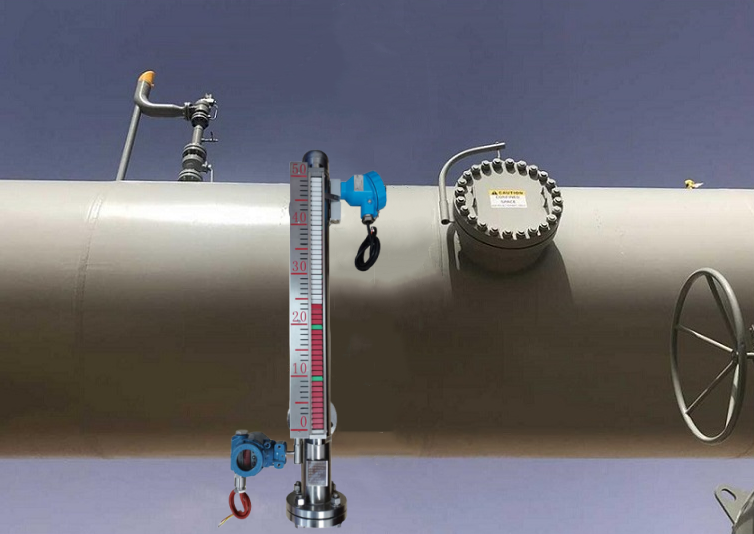

Magnetostrictive Level Gauge
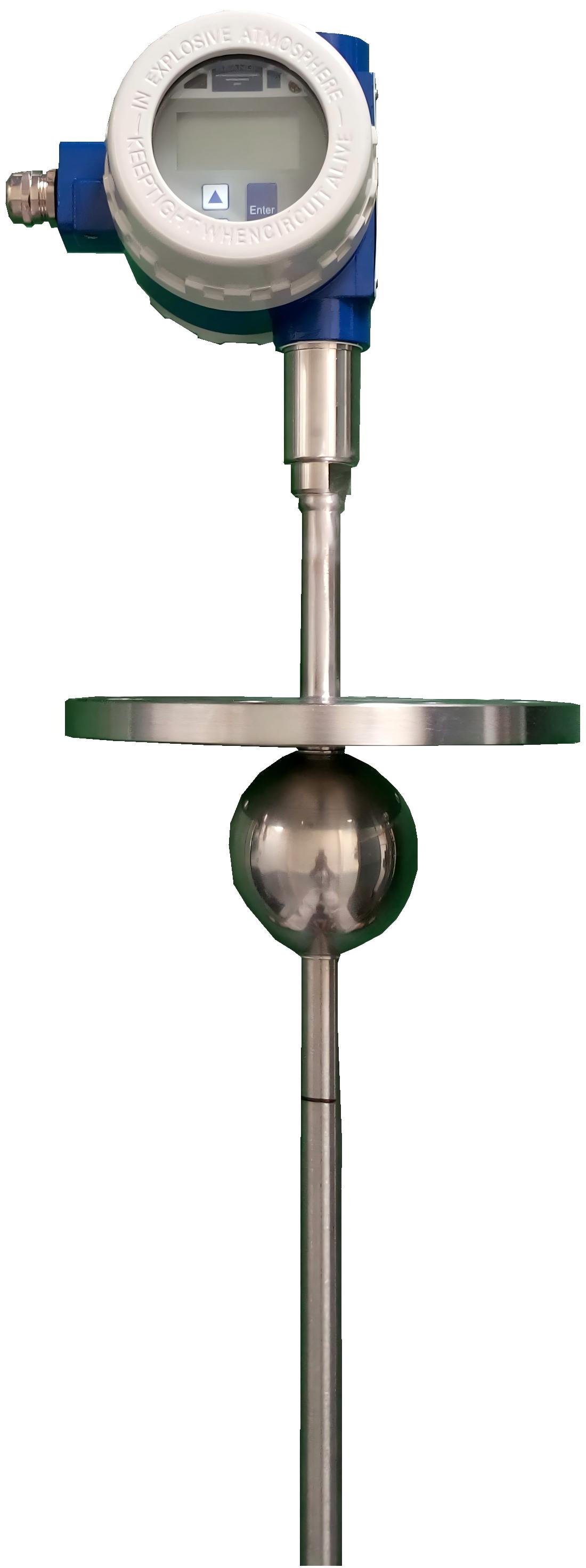

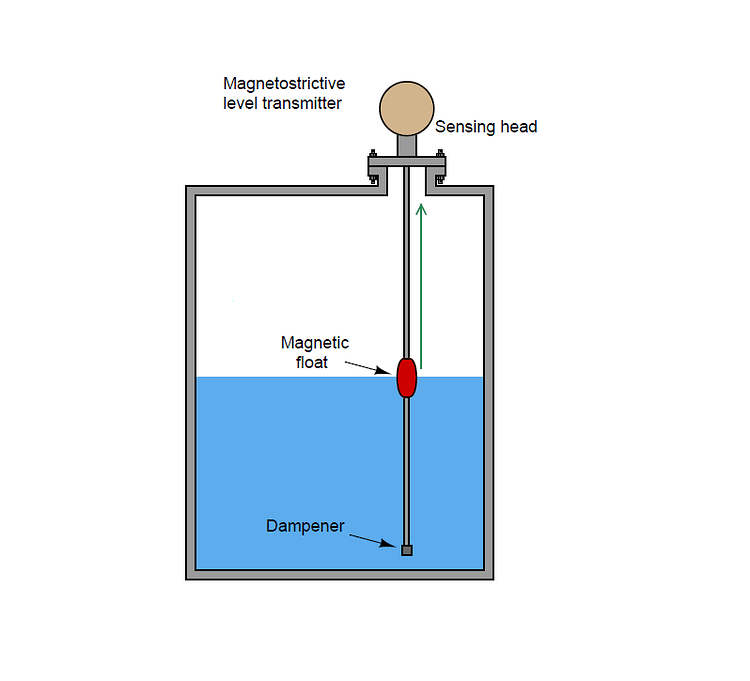
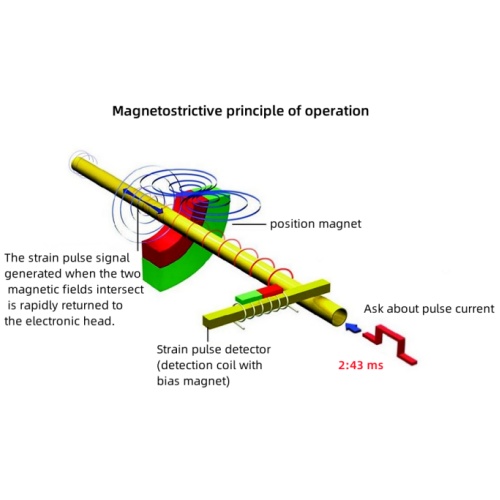
Magnetostrictive level gauges operate on the principle of the magnetostrictive effect. Their core component is a waveguide tube constructed from a conductive material, typically an iron-nickel alloy or other magnetostrictive material. When an electrical pulse passes through the waveguide tube, it generates a magnetic field around the tube. A magnetic ring embedded within the float generates a counteracting magnetic field. Where these two magnetic fields meet, a distortion wave is generated within the waveguide. This wave propagates along the tube wall and is ultimately detected by the sensor. By precisely measuring the time difference between the emission of the current pulse and the arrival of the distortion wave at the sensor, the position of the float can be determined, thereby calculating the liquid level height.
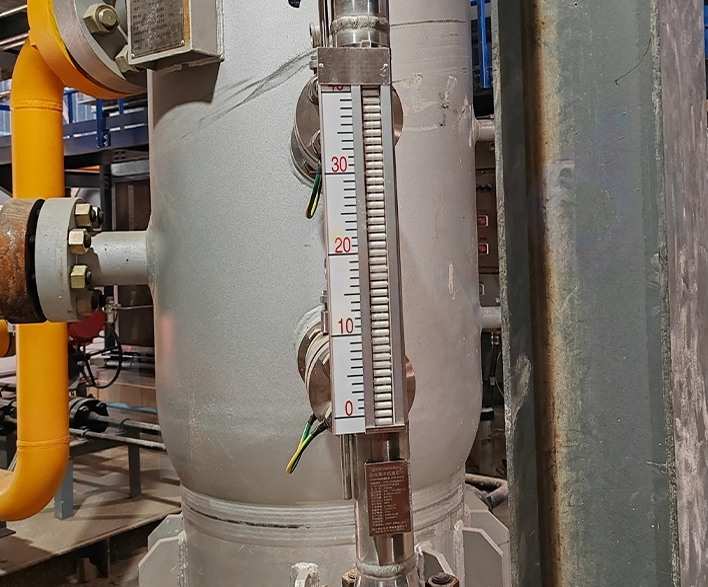
II. Application Scenarios and Advantages/Disadvantages
Magnetic Flip-Board Level Gauge
Magnetic flip-plate level gauges are typically employed for low to medium precision liquid level measurement applications. Owing to their simple construction, relatively low cost, and lack of power supply requirements, they are well-suited for scenarios lacking electrical infrastructure or demanding minimal maintenance, such as storage tank level monitoring and corrosive medium measurement in chemical plants. The primary drawbacks of this equipment are its lower accuracy and unsuitability for complex processes requiring precise liquid level control. Literature indicates that magnetic flip-plate level gauges maintain satisfactory performance even in harsh environments. Their corrosion resistance and mechanical stability contribute to their widespread application within the chemical and petroleum industries.

Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter
Magnetostrictive level transmitters, renowned for their high precision and resolution, find extensive application in sectors demanding exceptional accuracy in liquid level measurement, such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage industries. This equipment not only measures liquid levels with precision but also concurrently monitors the height of liquid interface layers, rendering it particularly suitable for processes involving multiple coexisting liquids. Its drawbacks include relatively high cost and the requirement for an external power supply alongside sophisticated electronic circuitry. Research indicates that magnetostrictive level gauges exhibit stable accuracy and repeatability during prolonged operation, rendering them favoured for demanding process control applications. Furthermore, with measurement precision reaching ±1 millimetre, these gauges demonstrate exceptional performance in monitoring oil and gas tanks.
III. Comparison of Accuracy and Reliability
Accuracy
Magnetic flip-plate level gauges typically offer measurement accuracy ranging from several millimetres to several centimetres, primarily dependent on the design and manufacturing process of the float and magnetic flip-plates. Magnetostrictive level gauges, however, can achieve accuracy of ±1 millimetre or higher, making them particularly suitable for applications where extreme sensitivity to liquid level changes is required.
Reliability
In terms of reliability, magnetic float level gauges possess high resistance to interference and durability owing to their absence of complex electronic components and relatively simple mechanical structure. They are suitable for corrosive media or high-temperature, high-pressure environments. Magnetostrictive level gauges, however, incorporate precision electronic components internally. Whilst offering higher measurement accuracy, their reliability in harsh environments may be inferior to that of magnetic float level gauges, necessitating thorough maintenance.
IV. Conclusion
Magnetic flip-plate level gauges and magnetostrictive level gauges each possess distinct advantages and suitable applications. The former is appropriate for less demanding scenarios with harsh environments, whilst the latter plays a vital role in high-precision liquid level measurement and complex process control. Industrial users should select suitable level measurement equipment based on specific application requirements, budget, and environmental conditions to ensure the safety and efficiency of production processes.
We are here to help you! If you close the chatbox, you will automatically receive a response from us via email. Please be sure to leave your contact details so that we can better assist